Which Accessories Are Must for Drone Enthusiasts?
Cricket cannot be played, or should we say that can't be played well in the absence of the right accessories. Just as the right accessories are needed
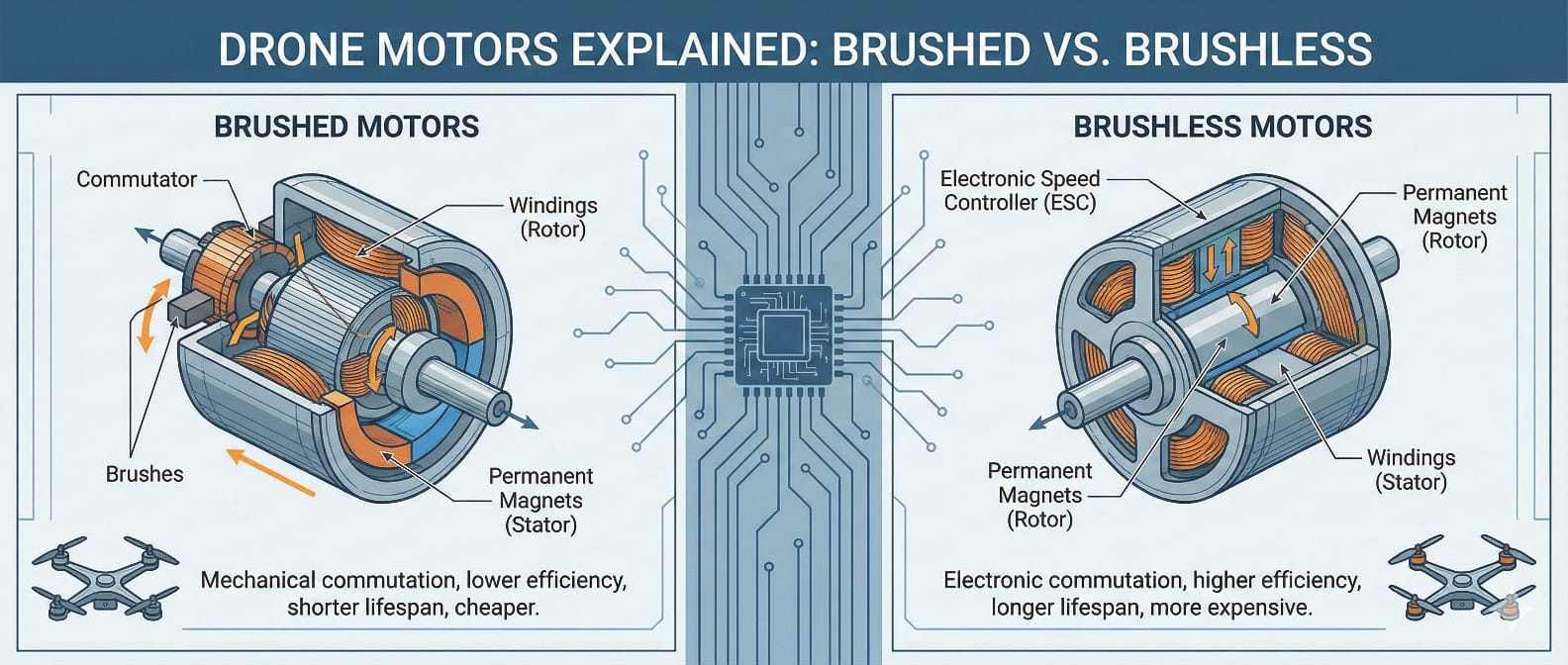
Drones are revolutionizing photography to agriculture, delivery and surveillance. Every drone is propelled by a motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical force. The choice between brushed and brushless drone motors affects the drone's performance, efficiency and longevity.
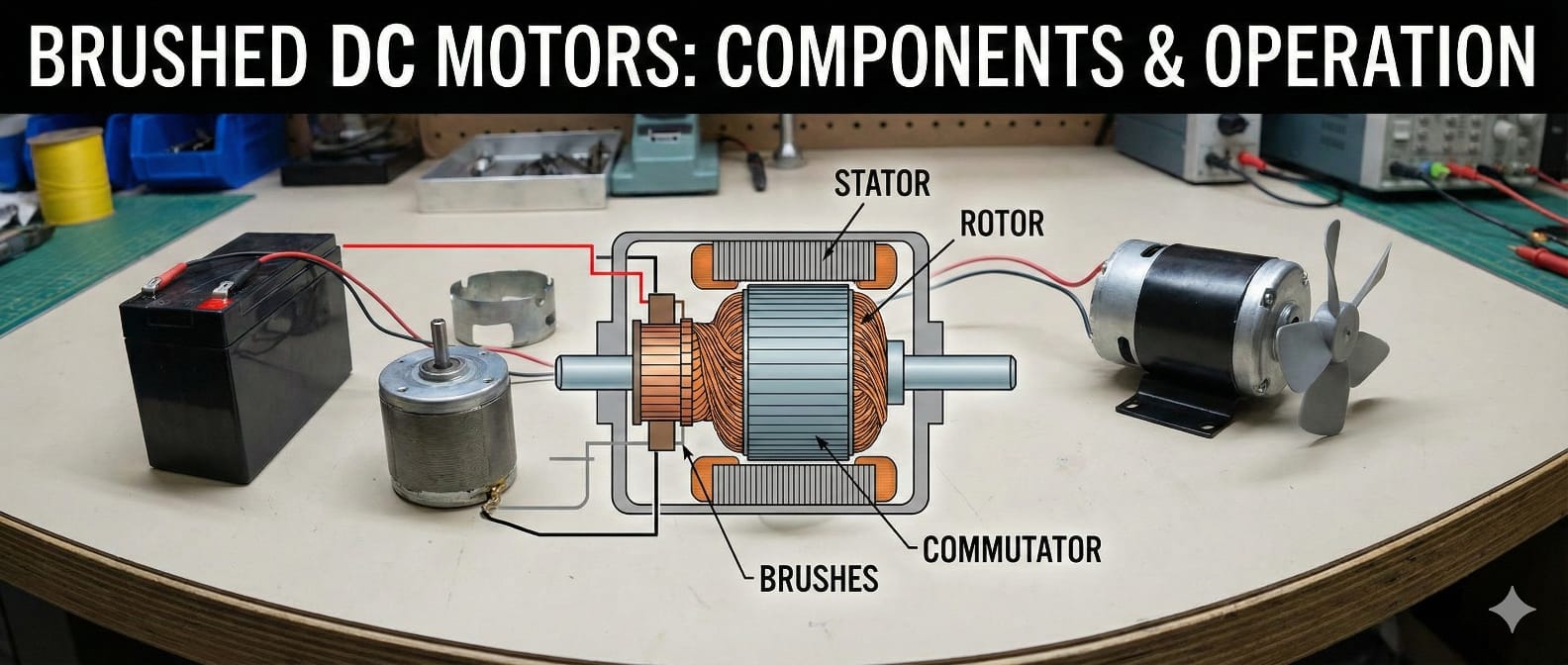
It is a type of motor that converts electric energy into mechanical energy by producing a magnetic field from direct current. The whole process uses brushes and a commutator to make a magnetic field and drive the rotor. The brushes are linked to the DC power source.
The motor has permanent magnets, known as the stator. The stator is stationary. The rotor or frame contains one or more electric windings that originally spin the motor at 180 degrees when external electrical current flows through them.
To allow continuous 360-degree rotation, carbon brushes flip the magnetic poles as the rotor turns. This is the simplest type of DC motor, frequently driven by batteries.

It uses electricity to create motion. The rotor has coils connected to the commutator. The commutator is in contact with brushes. These brushes stay in contact with the rotor as it spins, flipping the magnetic field and allowing it to complete a full 360-degree rotation.
Here is How it Work: The motor also has permanent magnets in the stator, which makes a strong magnetic field. As the motor moves, it reaches a point at which the brushes lose contact with the commutator, momentarily stopping the present flow.
The rotor continues to rotate until the brushes and commutator reconnect. When they make contact again, electricity flows into a diverse coil and the rotor continues spinning.

Cost-Effectiveness
These have a simpler design and manufacturing process. This helps lower operational costs, saving you money. This makes them a budget-friendly option for several applications, particularly when affordable solutions are needed.
Simple And Reliable to Use
These are easy to use because of their simplicity. They have just four main components: the stator, rotor, commutator and brushes. That makes them dependable and perfect for applications where elementary functionality and low cost are key priorities.
Ease of Control
They don’t need intricate electronics and are easy to control. Voltage needs to be adjusted, or one needs to know the basic switch function to regulate their speed and direction. You can integrate and operate the motor in any application.
Easy To Miniaturize
These can be easily arranged on any device. They have fewer parts and a rather simple design. It can be miniaturized for use in toys, tools and gadgets without losing performance.
Excellent Traction
Brushed DC motors provide great traction, particularly when high torque is required at low speeds. This makes it seamless for electric vehicles and machinery, where strong pulling power is vital for moving heavy loads competently.
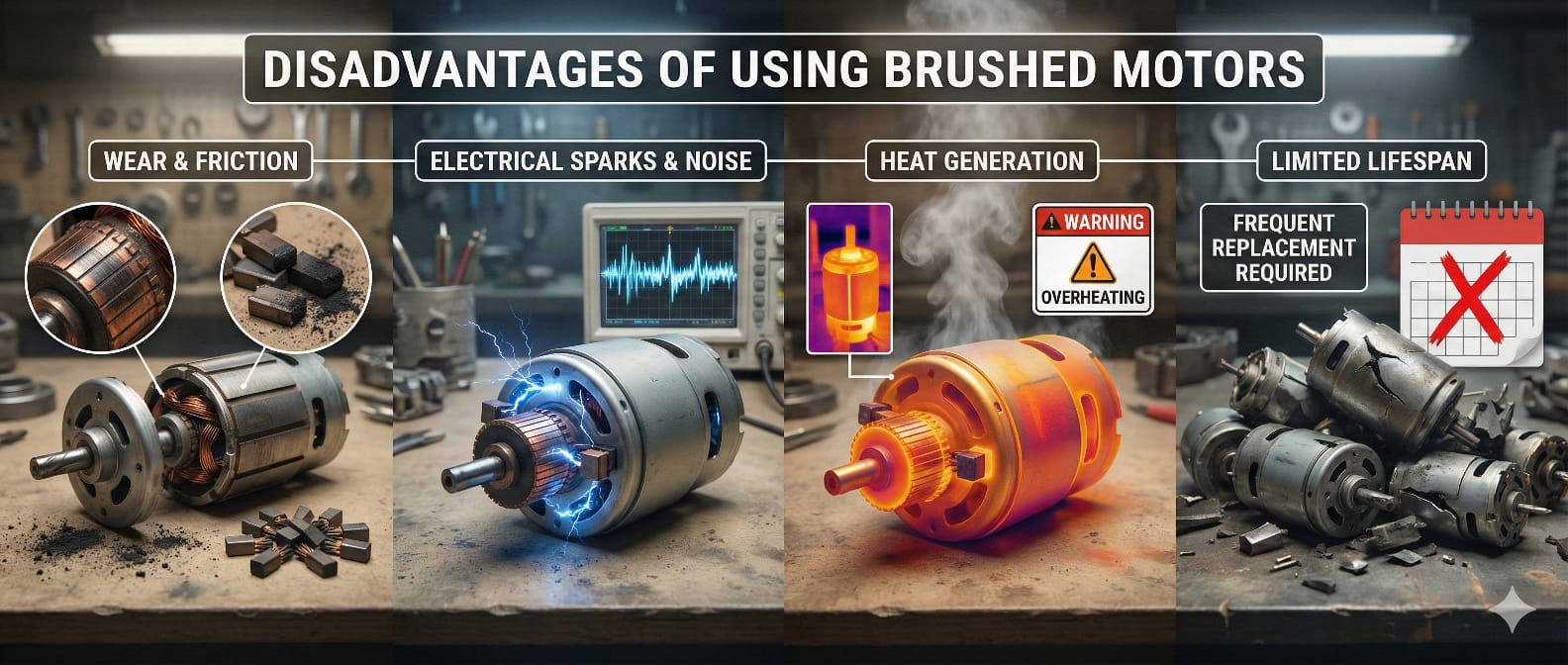
Mechanical Wear
One disadvantage of brushed motors is the mechanical wear of the brushes and commutator. The carbon brushes exhaust over time and need to be replaced regularly. That’s why they are intended to be replaced easily to guarantee maintenance is easy.
Electrical Noise
They can create electrical noise or electromagnetic interference. As the brushes and commutator work as switches, they generate sound. It sometimes affects nearby applications.
High Rotor Inertia
These have high rotor inertia, so their rotors resist rapid speed changes. They accelerate or decelerate rather slowly. However, it delivers up to 5 times the appraised torque without stalling and offers strong power.
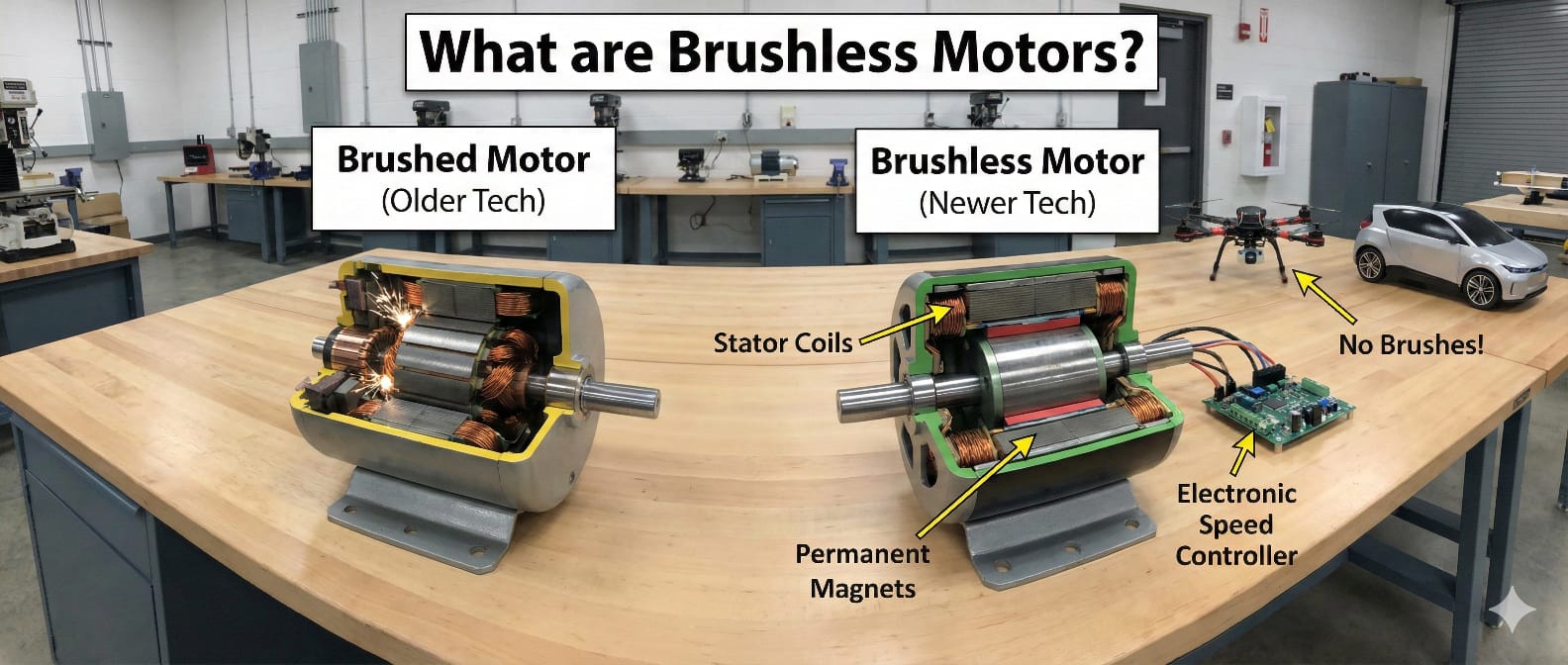
These DC motors have a permanent magnet rotor. The coils are fixed on the stator rather than rotating. So, there is no need for stator brushes or commutators as the stator does not move. Here, the stationary coils surrounding the coil produce magnetic fields. The rotation is attained by altering the direction of this magnetic field. You can regulate the strength and direction of the current in these coils. Therefore, you can regulate the movement of the rotor.

When the current moves through the stator windings, it produces magnetic fields. This magnetic field moreover entices or repels the magnets on the rotor.
The electric controller of the brushless motors switches the existing in the stator windings. These switching vicissitudes switch the direction of the magnetic fields around the stator. Accordingly, the rotor turns to align the stator-generated magnetic field.
The rotation of the brushless motors is measured by sequence and the timing of the electrical current sent to the stator coils. The electric controller regulates the speed and direction of the motor by adjusting which coils will be powered and when. It makes brushless DC motors more effective than brushed motors.
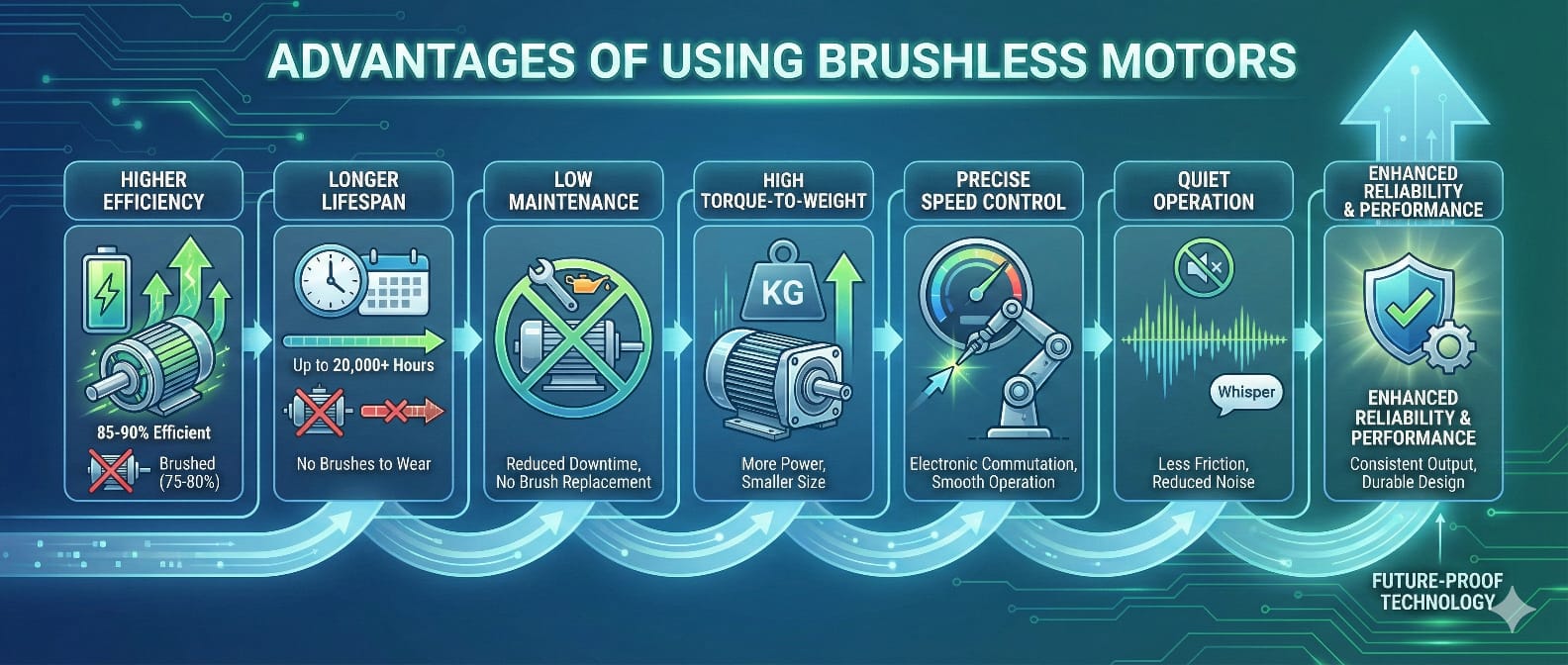
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Brushless motors can control the existing with electronic control and sensors. This accurate control improves the overall performance and competence. Brushless DC motors are 85% to 90% more effective than brushed motors, whose efficiency is about 80%. This higher competence results from reduced sound and heat, thereby reducing power loss.
Lower Maintenance Needs
These motors have carbon brushes that need to be replaced more often. Because brushless DC motors do not have brushes, they reduce maintenance requirements. This reduction in maintenance saves time and decreases costs more than the operational life of the brushless motors.
Compact Design with High Power
The brushless motor comes in several sizes. From the smallest to the largest, you can get what you require for your project. Brushless motors are powerful despite their small sizes. This motor's compact power is particularly valuable where space is limited, but high performance is required.
Wide Range of Applications
Brushless motors are lightweight. However, it can produce considerable torque output, approximately equivalent to that of larger induction motors. Furthermore, brushless motors offer performance, competence and longevity instantaneously. So, you can use them in handheld power tools and computer peripherals.
Flexible Customization Options
Owing to the high design flexibility of the brushless motors, they can be used in applications with different voltages, load requirements and rotation speeds. The motors can operate with or without sensors and have more poles than brushed motors.
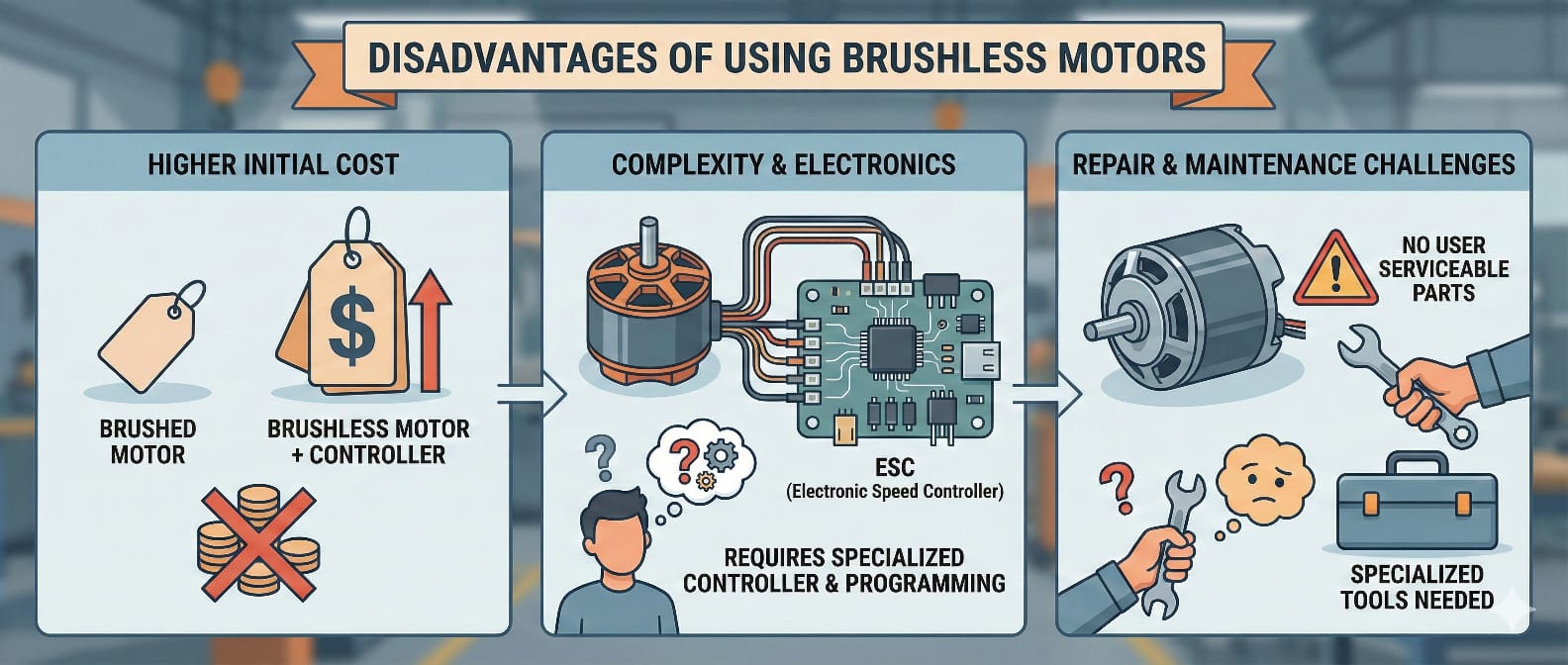
High cost
This motor needs a high-performance material. For example, high-temperature wear-resistant materials, rare-metal permanent magnets and so on increase the cost. That’s why the brushless motors are more expensive than their brushed counterparts.
Limited Range
These have a limited range as opposed to the brushed motors. In applications where high speed is vital, the brushless motors might not produce enough torque. This makes them inappropriate for some applications.
Requires cooling
The brushless motors might require cooling for high-power operation. The non-attendance of heat dissipation in the brushless motors can affect their performance in diverse applications.
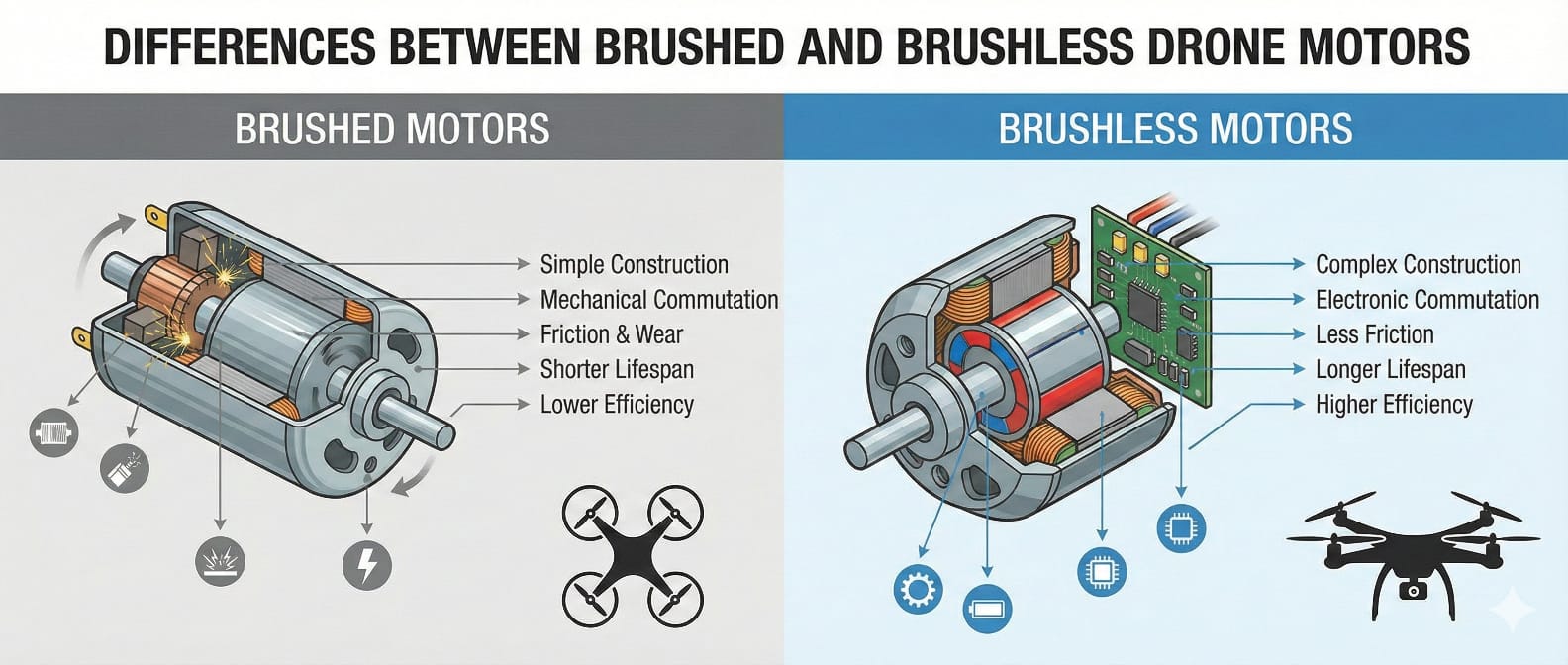
Operating Speed
These motors run at a speed at between 1,000 and 10,000 RPM. At higher speeds, the brushes can lose contact with the commutator, reducing performance. In contrast, brushless motors can work much faster. As they don’t rely on brushes, there is no risk of performance halting at higher speeds. This makes brushless motors perfect for high-speed applications.
Lifespan
Brushless motors have a much longer lifespan than their brushed counterparts. Over time, brushes in brushed motors wear out, limiting their lifespans to 2,000 to 5,000 hours.
Brushless motors often exceed 10,000 hours. As they don’t have brushes, their lifespan relies on the bearings and environmental conditions. That’s why it is a better choice for projects requiring long-lasting performance with nominal maintenance.
Cost
A brushed motor is much more economical than a brushless motor. The manufacturing steps are straightforward and the technology is well-established. So their cost is less. Although brushless motors need advanced electronics, which increase their costs, they have longer lifespans and lower maintenance requirements.
Power Density
Brushless motors have more power than their brushed counterparts. Brushed motors make use of mechanical brushes that contact the commutator. It generates friction, which eventually causes power loss. In contrast, brushless motors use cutting-edge electronic switches, like transistors, to regulate the flow of current to the motor’s windings. For this unique design, the motor doesn’t need physical contact, reducing friction and unwanted heat.
Torque Stability
Brushless motors have a lot more power than brushed motors. They offer higher torque and maintain consistent rotational power during operation. This makes it a perfect tool to use for several tasks. They have lower torque ripple, which decreases vibration and noise during operation. Instead, brushed motors can only attain maximum torque at precise points during their rotation.
Rotor Balancing
Brushed motors need regulating weights and rotor parts to balance the complete setup. This is significant for avoiding shaking or vibration when it moves. To do this, manufacturers add small weights, such as washers, or bend certain parts of the rotor. This guarantees the rotor’s centre is associated with the axis it spins on without any vibrations.
Electrical Noise
Brushed ones are noisier than brushless motors. The brushes touch the commutator as they spin, producing friction and noise. As the brushes deteriorate, the noise gets louder. Likewise, when the motor starts, it might spark or make noise.
Instead, brushless motors are usually quieter because there are no brushes that rub against the commutator. Also, when they spin faster, they can be louder because of air resistance and vibrations. However, they are generally quieter in applications, for example, disk drives and medical machines.
Thermal Management
Brushed motors produce more heat than brushless motors. The brushes and commutator in a brushed motor mainly create heat as the motor runs. This friction, combined with energy losses, causes the motor to become too hot, especially during prolonged use.
Compared to this, brushless motors are energy efficient. As they don’t feature brushes or a commutator, you won’t get any friction and energy loss as heat. This helps the brushless motor stay cooler, even when running at high speeds or for longer times. Their increased efficiency is around 85 to 90 per cent, making them a better choice for applications where there are concerns about high heat generation during operation.
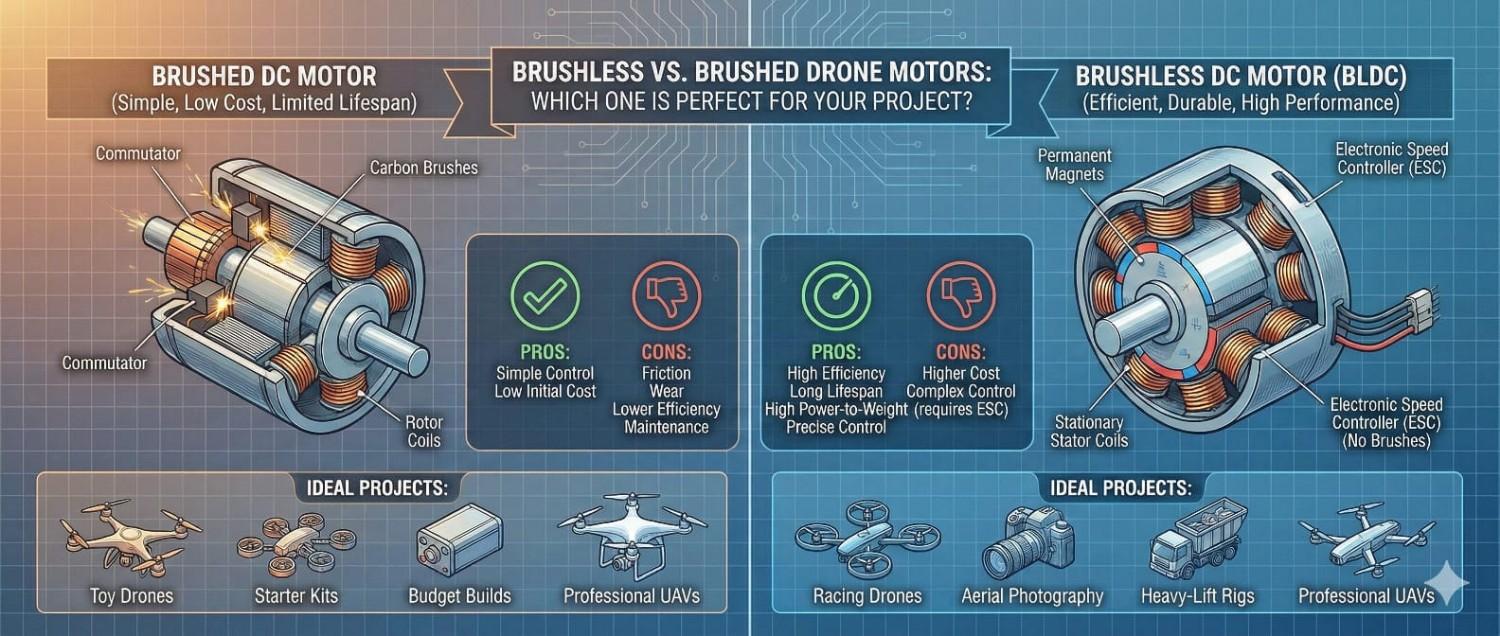
What you should choose between brushed and brushless motors mainly depends on your project’s needs. For instance, if you need a cost-effective solution in simple designs, a brushed motor is a good choice. You can easily use it for your household appliances, power tools, or even car window motors. These types of motors are easier to find and more affordable, but they require maintenance over time.
On the other hand, if you need higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and quieter operation, a brushless motor is a better option. They are great for applications like model aircraft, electric vehicles, robotics, and washing machines. These types of motors ensure long-lasting operation, produce less noise, and require less maintenance.

If you need a simple, inexpensive drone motor, a brushed motor is a good choice. But if your project needs high performance and precision or runs at high speeds, a brushless drone motor is better.Contact us at Flapone Aviation to select top-quality motors and find the perfect match for your project.
Not sure which drone fits your needs? Our experts can guide you to the perfect UAV for your mission.