Drone Laws and Regulations, Every Indian Pilot Should Know
Imagine if there were no rules and regulations to govern a discipline or profession, all would have ended up in an anarchy of sorts. This is the reaso
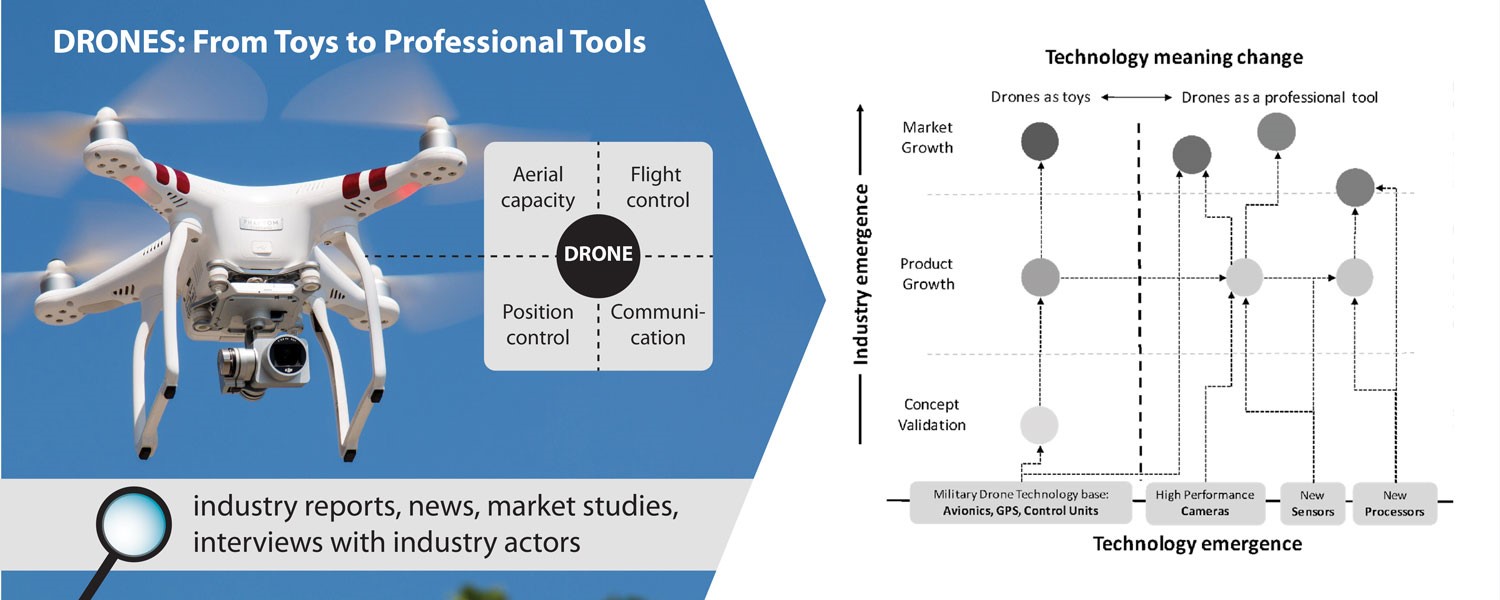
As drones become smaller and more maneuverable, law enforcement agencies are increasingly using them for enhanced safety and efficiency in their operations. From consumer models, such as the DJI Phantom’s GPS with GoPro action camera functionality, to enterprise-grade drones tailored precisely for police and first responders, law enforcement drones have been quickly accepted by all government agencies for law enforcement purposes.
Civilian drones are significantly more economical compared to helicopter rentals for aerial photography and video production. Drone cameras have electronic speed controllers that manage motor speed and direction to stabilizing gimbals, mitigating vibration and wind for sharp images. Some autonomous drones can avoid obstacles. Others boast cutting-edge features, including AI that allows them to follow subjects while recording video with audio commentary, or even provide AR capabilities that overlay virtual objects onto the live feed from the drone.
Drones are an indispensable military asset. While drones cannot replace human observation, their unique perspective lets commanders gain fresh perspectives and identify areas for improvement easily than before. Also, drones can gather intelligence about enemy locations. Military drones can carry out lethal strikes against targets, yet critics assert they violate international laws on extrajudicial, summary or arbitrary killing.
Civilian drones have become predominant for leisure use, including capturing aerial photos. Drones can also be used to record videos, audiovisual productions or virtual real estate tours. As stated by FAA regulations and any specific rules of any local airfield or controlled airspace they are flying over, including keeping within visual range of their pilot at all times, while not flying above 500 feet.

The very first pilotless vehicles were developed during the First World War. These radio-controlled aircraft were used as targets for training purposes. Drones then gained popularity as hobby gadgets, captivating enthusiasts with their ability to fly and capture stunning aerial photographs and videos. Early models were frequently small, toy-like devices with limited competencies and flight times. With increasing interest, manufacturers have documented the possibility and begun manufacturing more accessible and trailblazing drones custom-made for photography and videography.

With the progression of drone technology, its potential for commercial applications became evident. Agriculture, construction, filmmaking and surveying, rapidly realized the benefits of making use of drones. In agriculture, drones equipped with cameras and sensors have revolutionized crop monitoring, enabling farmers to assess plant health, identify problem areas, and optimize resource allocation.
In construction, drones have updated surveying and mapping processes, improving accuracy and competence on job sites. Filmmakers utilize drones to capture spectacular aerial shots, a feat once only possible with helicopter rentals. Drones can also be used in disaster management, search and rescue operations and infrastructure inspection, transforming the way these tasks are conducted.

The expansion of drones has brought about progressions in several areas. Battery life has been enhanced, allowing for longer flight times and increased operational range. Lightweight materials and compact designs made drones more portable without forfeiting performance. GPS incorporation is permitted for detailed navigation and autonomous flight competencies. The overview of obstacle avoidance systems and collision sensors improves safety and dependability. Furthermore, progressions in camera and imaging technology have led to high-resolution imagery that can capture thermal or multispectral data, unlocking novel possibilities in agriculture, environmental monitoring and public safety.
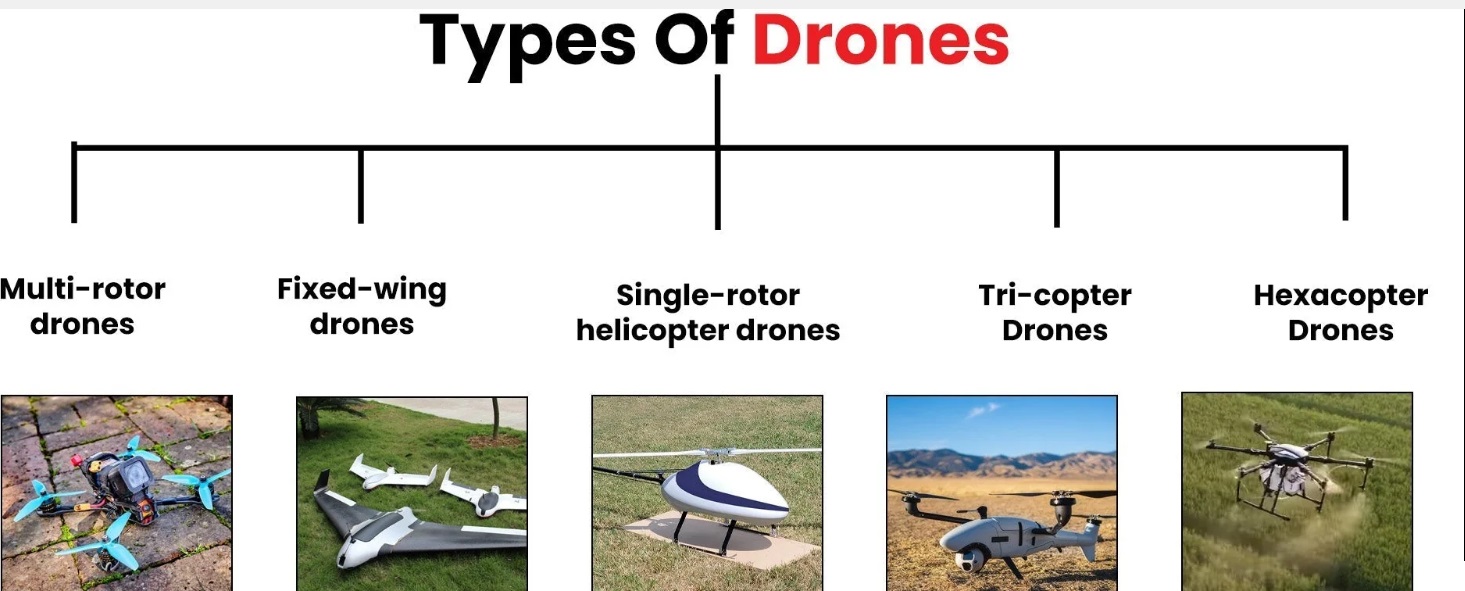
As drones soared in popularity, governments worldwide recognized the need for regulations to guarantee safe and responsible usage. Regulatory frameworks have been developed to address concerns regarding privacy, airspace congestion, and the potential drone misuse. They comprise guidelines for drone registration, pilot licensing, flight restrictions and working limitations. While navigating these procedures can be thought-provoking, they also provide a framework for the safe incorporation of drones into society and the understanding of their full potential.
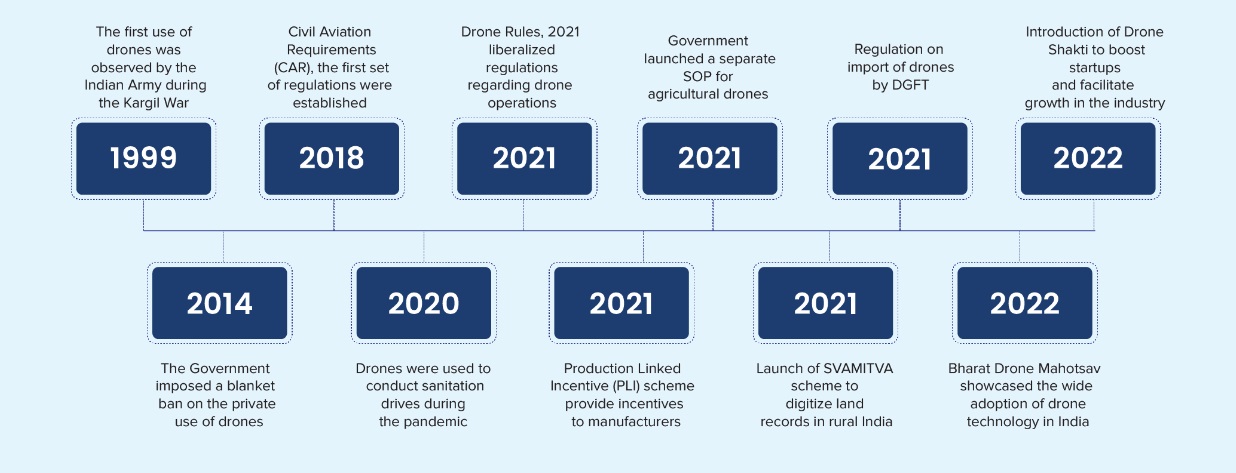
Progressions in battery technology have enabled drone advancements, allowing for longer runtime between recharges. An increase in capacity and power has enabled drones to travel greater distances while carrying heavier payloads, leading to widespread acceptance across both commercial and recreational markets.
Military drones were advanced during World War II to spy on enemy forces. These drones used a camera for vision and a radio transmitter for communication with pilots on the ground. Additionally, these could only operate within sight, being controlled by a crew of control aeroplanes with Tommy guns.
Archibald Low, a British engineer, advanced an advanced drone in the mid-20th century. Intended as an experiment-observation replacement throughout experiments at Royal Aircraft Establishment, Low’s drone flew over 10,000 times with researchers operating it and with barometric sensors that measured air pressure for altitude control, along with gyroscopes that controlled pitch and yaw, plus magnetic compasses for navigation purposes.
Recent drone expansions comprise trailblazing sense-and-avoid systems that allow drones to autonomously navigate and avoid obstacles in their flight paths, thus reducing collisions among drones and other aircraft or objects.

The expansion of drones shows no signs of slowing down. Sustained developments in AI, ML, and sensor technologies are revolutionizing drones even further. Swarm intelligence, where multiple drones cooperate and communicate to accomplish intricate tasks, is being explored. Drone delivery services, independent aerial taxis and urban air mobility concepts are transforming transportation and logistics. Moreover, drones are important in 5G network maintenance, environmental monitoring and even space exploration.
From recreational toys to drones, these devices have evolved across several industries, transforming the way we approach tasks. As we observe the ongoing developments and innovations in drones, we can anticipate further advances that will shape the future.

If you want to enter the world of drones and drone training, you can enter a drone piloting school. It is not just about drone training, but also about purchasing various kinds of drones. At Flapone Aviation, we are pioneers in drone training and services, and we will help you live the dream of becoming a renowned drone pilot.
Not sure which drone fits your needs? Our experts can guide you to the perfect UAV for your mission.